Understanding The Modern Web Solution Stack
Tim Williams • March 28, 2015
A web solution stack is a group of technologies that when combined, create the backbone for a modern web application. Understanding the stack as a whole and how to use each technology best is very important for a ‘full-stack’ web developer. With the recent emergence of JavaScript libraries like AngularJS and Ember.js the placement of business logic in web applications has now become a slightly more murky topic. It may be as few as 5 years ago that any web developer would tell you that there is one location for business logic in all web applications; the server. Thankfully due to these new JavaScript technologies web developers have the opportunity to now easily build applications that move a good portion of the business logic to the client. I believe that this is the future of web technology, in as few as 5 years the responsibility of the server will be relegated to mostly data persistence.
Let’s look at the current types of web solution stacks in use today and how business logic applies to each layer.
The Classic Stack
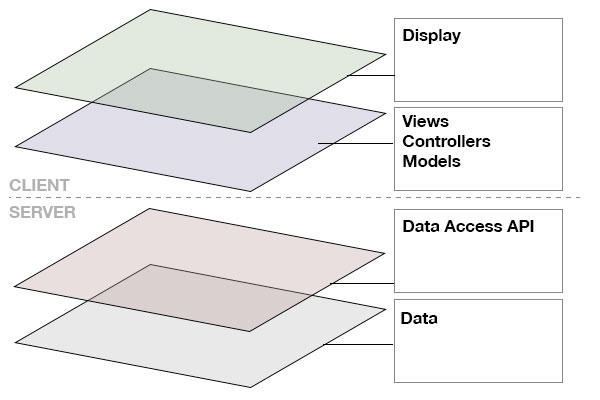
I call the this the “classic” stack because this is where the evolution started. In the classic stack the server contains ALL of the business logic of your application. The classic stack does not have to follow the MVC pattern, but this is the most common pattern found in modern web applications for separating responsibilities. Here’s more information on the MVC design pattern if you are not familiar with it.
The client is responsible for displaying the views and handling post requests via standard HTML forms. The server is responsible for all of the business logic including inferring the intent based on the HTTP request path or input, processing the data using models and putting the response back into a view or other type of output. Yes, I know, that’s an oversimplified explanation, but let’s not get bogged down in how an MVC works. 🙂
The classic stack is in my opinion the most limited approach with numerous performance drawbacks. By nature, the web works differently from other types of applications because there is very little in the way of state persistence between HTTP requests. In the classic stack, every piece of output must be rebuilt from scratch on every request to the server. When applications get more complicated such as having users with different capabilities and levels of access, objects with many relationships, or views which manipulate different objects things get very complicated very quickly.
Between each request the server must start from scratch to build the user’s state which might require multiple instances of access to the data layer and the instantiation of many objects which may have complex relationships to build a complete view output. Take these requirements into context and think about the most common requests made; to access a page with a list of objects, to see a single object for manipulation or to simply receive a message that says the object you just saved, was saved. These simple requests require most of the logic of the more complex requests which means every interaction with the server becomes slower, more complicated and more prone to error with every new feature. Luckily for users and developers alike, these types of web applications are going out of style quickly!
The Hybrid Stack
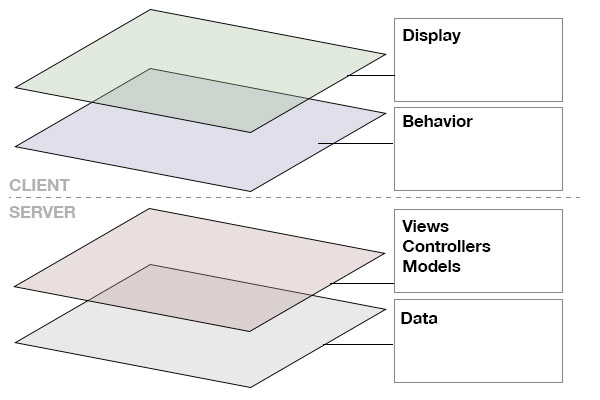
Enter; the hybrid stack. This stack is the evolutionary response to the problems with the classic stack. In this design pattern the client is taking on slightly more of the responsibility adding on a little more AJAX requests to the server to display things like status updates, and simple transactions. This removes the necessity of complete state persistence between requests. This allows for a simple task to have a simple response. I don’t need to build your complicated context menu again, just because you saved your object!
BE CAREFUL! The hybrid web stack can get out of hand quickly if clear decisions are not made on what layer owns what piece of responsibility. It becomes tempting to start leaking business logic into the clients behavior layer! This can cause many principles like DRY to be accidentally broken more easily. For instance, is form validation now the responsibility of the client? The server? Both? 😐
The hybrid stack has clear advantages then, state persistence becomes less of an issue, and the burden on the server can be marginally lessened. The biggest downside is that this is the most complicated pattern, as it becomes hard to decide where logic goes and later, where to find it!
The Client Stack

Finally, I’m proud to present my favorite; the “client” stack. This pattern has been gaining a lot of popularity with client side MVC solutions becoming available as viable, well documented, and wonderfully open source solutions. This pattern pushes your business logic into the client layer eliminating the most annoying inherent problem in web development; state persistence. There are many new client stack flavors the most radical of which are using websockets to provide data persistence allowing for truly real-time applications to be possible.
I believe this pattern is the future of web development because it provides solutions to some of the most annoying problems facing developers. It clearly defines what stack layers are responsible for each piece of logic. The client is responsible for object manipulation, behavior and all aspects of view output. The server is used possibly through a RESTful API, or a more radical solution like websockets to provide data layer object persistence.
Though I wanted to keep this on mainly a conceptual level, not diving into the technologies that typically make up these new design patterns, I’m excited about the prospect of this evolutionary leap in web technology! Some of the leaders of the pack (who may well be ahead of their time) are adopting cutting edge technology like the MEAN stack to build apon this idea of pushing the power to the client.
My vision of the Web 3.0 is a web that feels like a desktop application, things happen in real-time. The beauty of it is, this style of development is open to us today! Single Page Applications are real, and will be demanded by consumers and clients once the benefits become clear.
So? What do you think?
